China

National Flag
The People's Republic of China (PRC) commonly known as China, has control over mainland China and the largely self-
governing territories of Hong Kong (since 1997) and Macau (since 1999). China, the world's third largest country spans
about 2,500 miles (4,023 kilometers) from north to south, and approximately 3,000 miles (4,828 kilometers) from east to
west. The metropolitan area of Shanghai is second largest with more than 13 million people, and Beijing ranks fifth in the
world with almost 11 million.
On 1 January 1912, the Republic of China was established, heralding the end of the Qing Dynasty. On 1 October 1949, they
established the People's Republic of China as a Socialist State headed by a “Democratic Dictatorship” China, a huge
country in eastern Asia, is the world's third largest nation in area and largest in population. About 20 per cent of the
world's people live in China. Today, mainland China is administered by the People's Republic of China – a one-party state
under the leadership of the Chinese Communist Party while the island of Taiwan and surrounding islands are
administered by the Republic of China a democratic multi-party state. In the central-east are the deltas of China's two
major rivers, the Huang He and Yangtze River. Most of China's arable lands lie along these rivers to name a few which
include the Pearl River, Mekong, Brahmaputra and Amur.

Emblem
Profile:
Official Name - People's Republic of China
Nationality - Chinese
Chief City - Beijing
Location - East Asia
Population - 1,321,851,888 (1st)
Area - 9,640,821 km
Official Languages - Chinese
Government - Socialist state, Single, party communist state
Currency - Yuan (CNY)
Map
national anthem
Qǐlai! Bùyuàn zuò núlì de rénmen!
Bǎ wǒmen de xuèròu, zhúchéng wǒmen xīn de
chángchéng!
Zhōnghuá mínzú dàoliao zuì wēixiǎn de shíhou.
Měi ge rén bèipòzhe fāchū zuìhòu de hǒushēng.
Qǐlai! Qǐlai! Qǐlai!
Wǒmen wànzhòngyīxīn,
Màozhe dírén de pàohuǒ, qiánjìn!
Màozhe dírén de pàohuǒ, qiánjìn!
Qiánjìn! Qiánjìn! Jìn!
TRANSLATION
Arise! All who refuse to be slaves!
Let our flesh and blood become our new
Great Wall!
As the Chinese nation faces its greatest peril,
All forcefully expend their last cries.
Arise! Arise! Arise!
Our million hearts beat as one,
Brave the enemy's fire, March on!
Brave the enemy's fire, March on!
March on! March on! On!
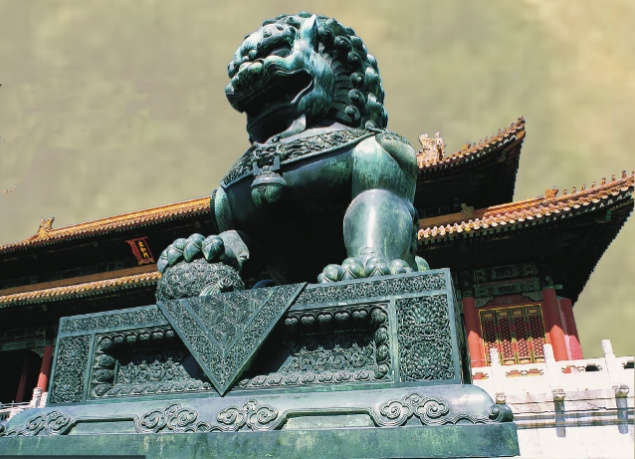

Imperial Palace Beijing China
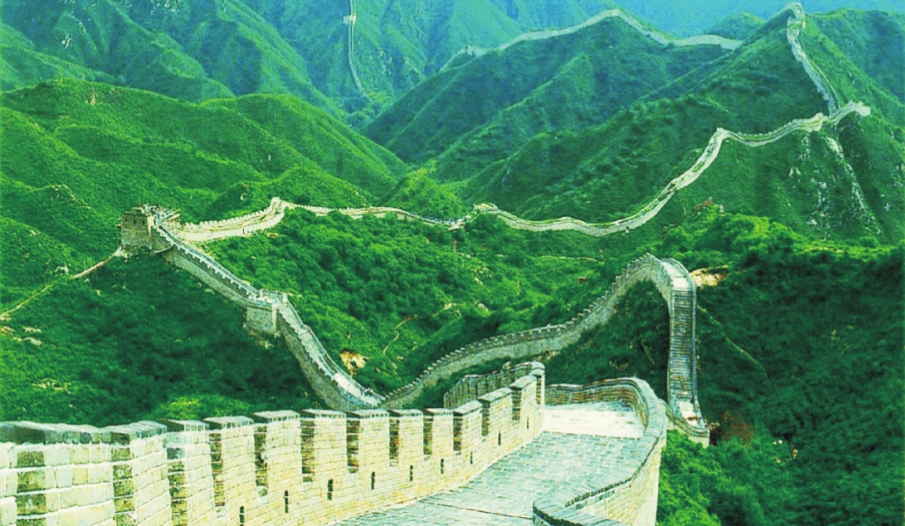


Great wall of china
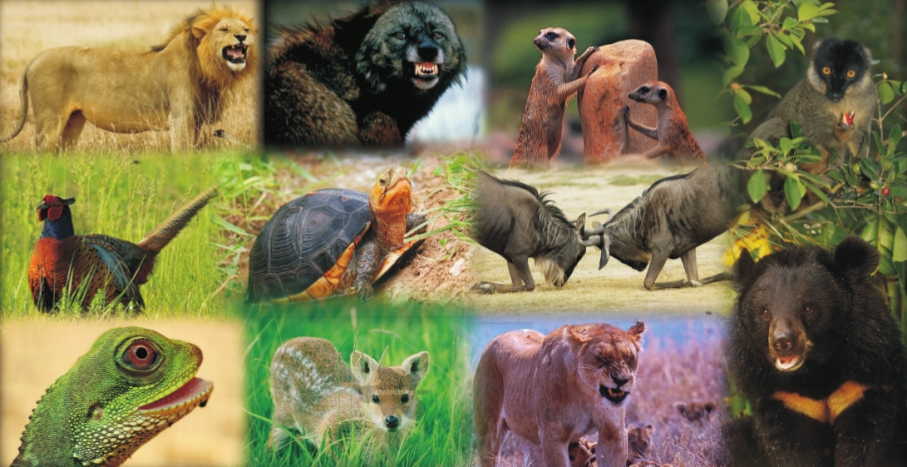

Wildlife

Ming & Qing Dynasty, Hall of Supreme Harmony, Palace Museum, Forbidden City, Beijing,

The Hui Community, Chinese cooking wok noodles
culture
Chinese philosophers, writers and poets were highly respected and played key roles in preserving and promoting the culture of the empire. The Chinese invented numerous musical instruments, such as the zheng, qin, sheng, and xiao. Many Han people – both city and rural dwellers – perform ancient Chinese exercises called taijiquan every morning. Taijiquan emphasizes relaxation, balance, and proper breathing techniques. Both men and women usually dress in Western style shirts and loose-fitting trousers, and generally prefer short hair styles.
languages
Most languages in China belong to the Sino-Tibetan language family. All the Han people speak Chinese, but spoken Chinese has many dialects that differ enough in pronunciation to be considered separate languages. About 70 per cent of the nation's people speak Mandarin, or putonghua (common language), the country's official language. Other major dialects include Wu (spoken in Shanghai) and Yue (also called Cantonese).
sports
Many historians believe that football (soccer) originated in China; other popular sports include martial arts, table tennis, and badminton. There are also many traditional sports. Chinese dragon boat racing occurs during the Duan Wu festival.
people
China has the world's oldest living civilization, and a long history that goes back about 3,500 years. The Chinese were the first people to develop the compass, gunpowder, movable type, paper, porcelain, and silk cloth. China has more than 1 billion people, and about 94 per cent of them belong to the Han ethnic group, which has been the largest nationality in China for centuries. The Chinese call themselves Han people in recognition of China's achievements as during the Han dynasty. In general, people in China's urban areas have a higher standard of living than people in the countryside. About 75 per cent of China's people live in rural villages and small towns.
climate
This vast country is marked by an extraordinary variety of climates and landscapes. China's climatic regions range from tropical conditions in the southeast to severe, freezing weather in the north, and its landscapes range from some of the world's driest deserts and highest mountains to some of its richest farmland. The beautiful limestone hills near the city of Guilin on the Li River are among the most unusual features of this enormous country.
religion
The “official” orthodox faith system held by most dynasties of China centering on the worship of “Heaven” or Shangdi (literally “Emperor Above”) as an omnipotent force. Worship of Heaven includes the erection of shrines, the last and greatest being the Altar of Heaven in Beijing, and the offering of prayers. Taoism is an indigenous religion of China. Buddhism in China was first introduced from India and Central asia during the Han dynasty. Buddhism is the largest organized faith in China. Many Chinese, however, identify themselves as both Taoist and Buddhist at the same time. Ancestor worship is a major religious theme shared among all Chinese religion. Traditional Chinese culture, Taoism, Confucianism, and Chinese Buddhism all have love and respect for one's parents and ancestors. Chinese people generally offer prayers and food for their ancestors, light incense and candles, and burn offerings of Joss paper. These activities are typically conducted at the site of ancestral graves or tombs, at an ancestral temple, or at a household shrine.
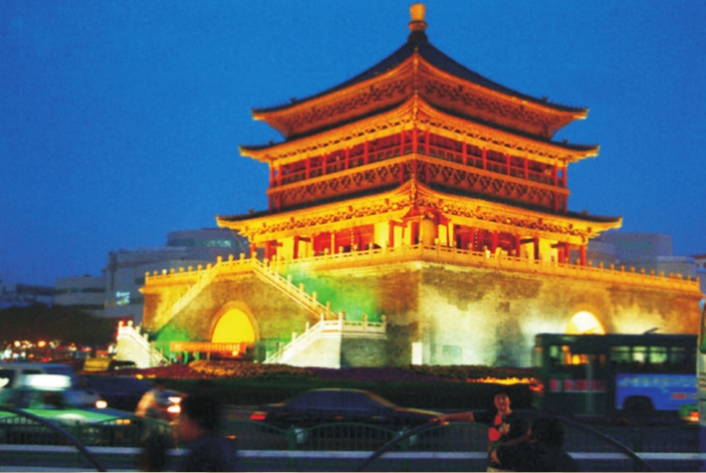

Bell Tower
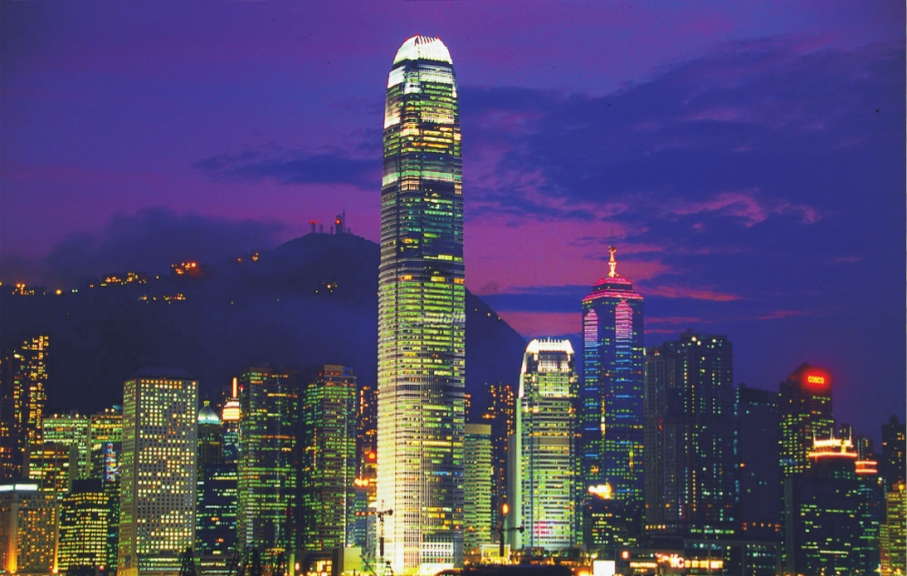

Hong Kong illuminated Skyline at night

Aerial View of Shanghai Skyscrapers

Wheat farming in China
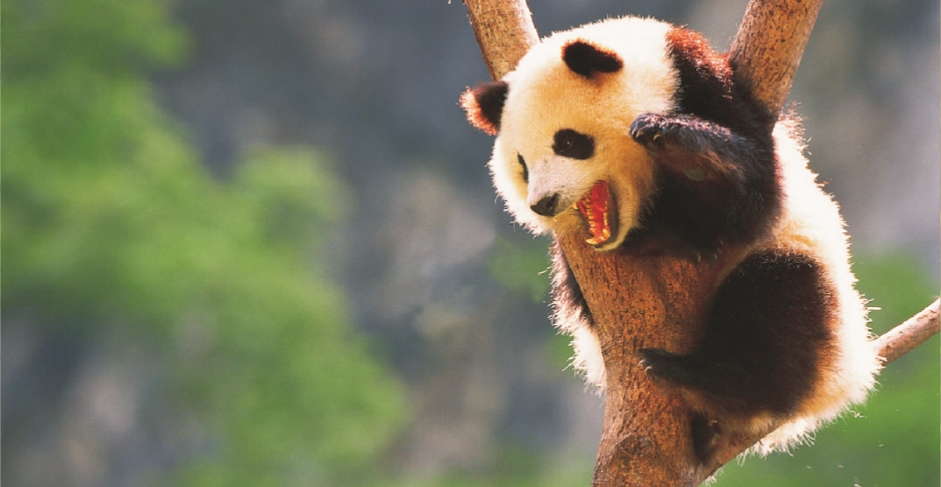

Giant Panda
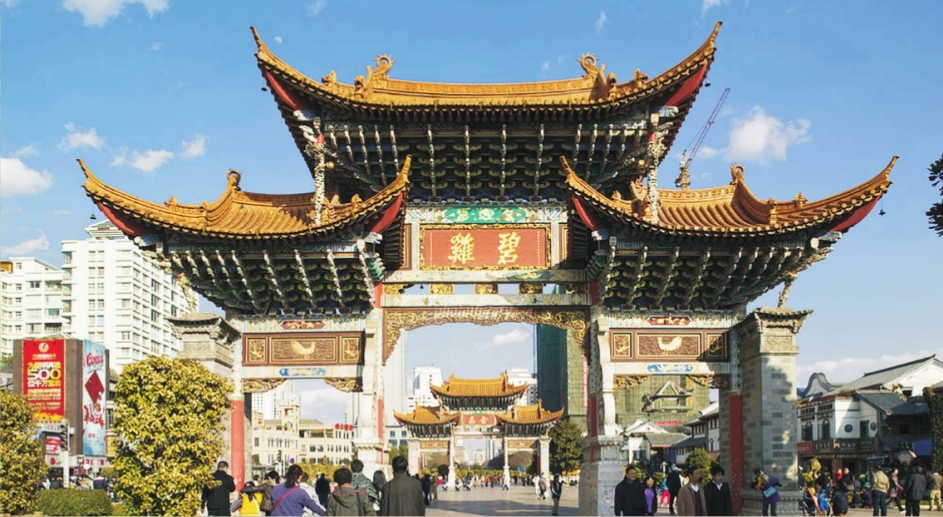

Memorial arch of the Golden Horse and Jade Rooster in Jinmabiji Square
sculpture and pottery
The oldest known Chinese works of art include pottery and jade carvings. After Buddhism reached China from India during the Han dynasty (22 B. C. A.D. 220) sculptors carved images of Buddha to decorate the temples. Some of these sculptures were made of stone or clay, while others were cast in bronze and coated with gold. As early as the 5000's B.C. (Chinese potters decorated their works with sophisticated painted designs. Painting on silk has been an art in China since about 400 B.C., while painting on paper began later.
the great wall
The Great Wall of China is the only man made object visible from the moon. With a total length of about 4,000 miles (6,400 kilometers) it is the longest structure ever built and was erected entirely by hand. Today, the Great Wall is truly one of the treasures of world civilization. Views of the Great Wall from various locations are a reminder of its enduring significance. The wall is even visible from outer space; a graceful watch tower marks the western end of the wall. A restored section near Badaling, once defended a strategic mountain pass and now fascinates visitors. Thousand of tourists from China and other countries come to see the wall every year. The Great Wall is also of interest to historians, who study the structure's fortifications, and to scientists, who study the effects of earthquakes on the wall.
wildlife
The takin, a mammal that resembles a musk ox, inhabits the dense bamboo forests of central, western, and southwestern China, and the Himalaya. The Chinese alligator and the giant salamander live in the Yangtze River Valley. The giant panda, a black-and-white bear like animal, lives only in western and southwestern China.

corner tower forbidden city
beijing
Beijing, also spelled peking, is China's capital and second largest city with a population of about 6 million residents. The Forbidden City and the Imperial City lie within the Inner City. The Forbidden City includes the palaces of former emperors. Only members of the emperor's household could enter the Forbidden City - hence its name. The Imperial City, which surrounds the Forbidden City, includes lakes, parks, and the residences of China's Communist leaders. The Temple of Heaven, where Chinese emperors used to pray for a good harvest, stands at the southern end of the Outer City.
economy
Agriculture is the foundation of China's economy, and about 70 per cent of all workers are farmers. In southern China, rice, sweet potatoes, and tea are the major crops. Wheat is the chief crop in the north, followed by corn and kaoliang (sorghum). In addition, it is also a leading producer of apples, cabbages, carrots, corn, melons, rubber, sugar beets, sugar cane, tomatoes. Agricultural output doubled in the 1980s, and industry also posted major gains, especially in coastal areas near Hong Kong and opposite Taiwan, where foreign investment helped spur output of both domestic and export goods.
cuisine
Chinese like to have their dinner together with all family members. They use chopsticks for eating rice. Chinese food is very famous all over the world.


